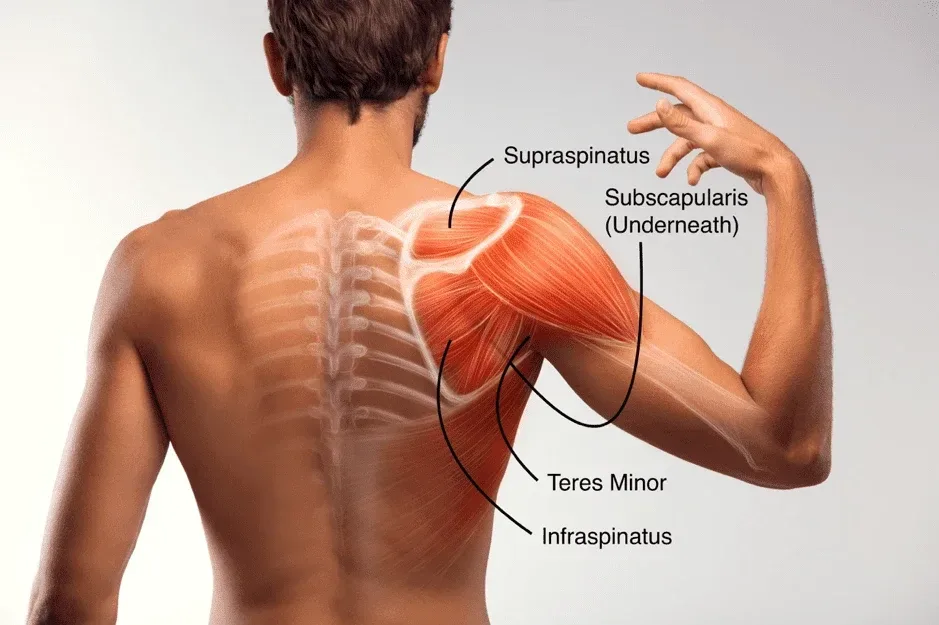
Rotator cuff tendinitis is a painful condition that affects the shoulder. It occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff become inflamed or irritated. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint and allow for a wide range of motion.
The main symptoms of rotator cuff tendinitis include pain and tenderness in the shoulder, especially when reaching overhead or behind the back. The pain may also radiate down the arm and worsen at night. Weakness and stiffness in the shoulder are also common.
Repetitive overhead motions or prolonged shoulder positions often cause rotator cuff tendinitis. Some common causes include:
Treatment for rotator cuff tendinitis typically involves a combination of rest, ice, and physical therapy. Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, a doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections or surgery.
Physical therapy is an essential part of treatment for rotator cuff tendinitis. A physical therapist can teach stretching exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles and improve shoulder mobility. They may also use ultrasound or electrical stimulation techniques to reduce pain and inflammation.
To help prevent rotator cuff tendinitis, it’s vital to maintain good posture and avoid repetitive overhead motions whenever possible. Taking frequent breaks and stretching the shoulder muscles can also help. If you participate in sports that involve throwing or overhead motions, be sure to use proper technique and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your activities.
If you experience shoulder pain or weakness that persists over a few days, it’s important to see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening and improve your chances of a full recovery.