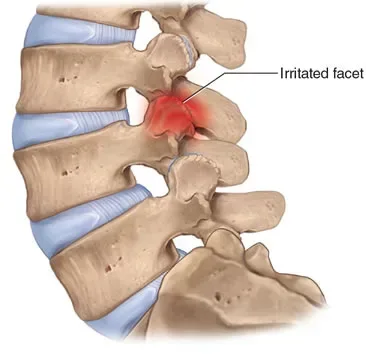
Facet dysfunction, also known as facet joint syndrome, is a common cause of back and neck pain. The facet joints are small stabilising joints located between and behind adjacent vertebrae in the spine. They allow for flexibility and motion while also providing stability to the spinal column. Facet dysfunction occurs when these joints become inflamed or degenerate, leading to pain and discomfort.
Several factors can contribute to the development of facet dysfunction. Age-related wear and tear is a common cause, as the cartilage within the facet joints gradually deteriorates over time. This can lead to osteoarthritis of the facet joints. Other potential causes include:
The symptoms of facet dysfunction can vary depending on the location of the affected joint. Common symptoms include:
The treatment for facet dysfunction typically involves a combination of conservative measures aimed at relieving pain and restoring function. These may include:
In cases where conservative treatments are not effective, surgical intervention may be considered. This could include procedures such as a facet rhizotomy, where the nerve fibres causing pain are destroyed, or spinal fusion, which stabilises the affected segment of the spine.
Preventing facet dysfunction involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, proper nutrition, and maintaining a healthy weight. Attention to posture and ergonomics, especially during physical activities and desk-bound tasks, can also play a crucial role in preventing facet joint strain and degeneration.
For more detailed information on facet dysfunction and its management, refer to authoritative sources such as medical textbooks or reputable medical websites.